CASTINGS
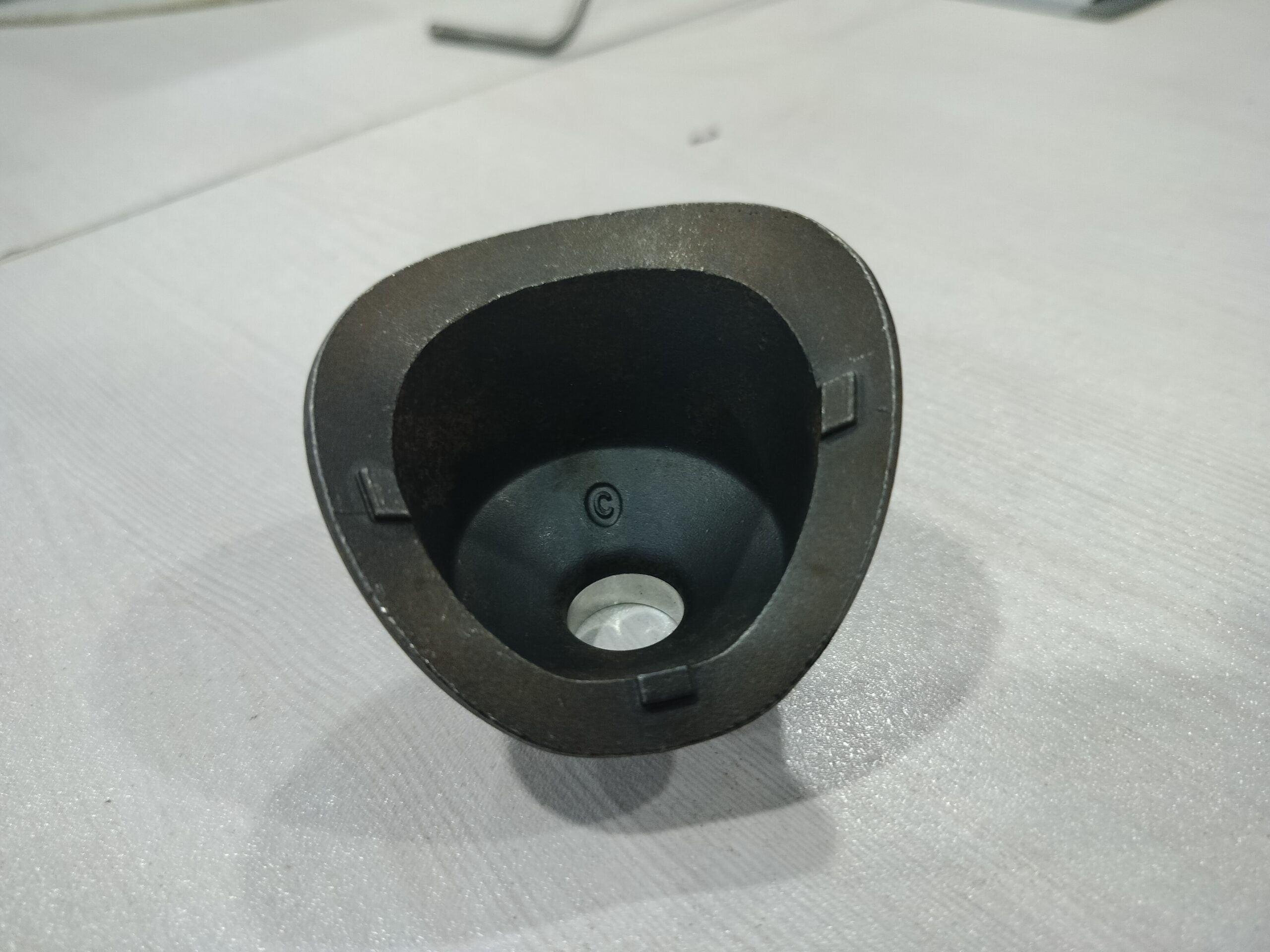

Centrifugal Casting (Industrial) – Centrifugal casting or rotocasting is a casting technique that is typically used to cast thin-walled cylinders. It is typically used to cast materials such as metals, glass, and concrete. A high quality is attainable by control of metallurgy and crystal structure. Unlike most other casting techniques, centrifugal casting is chiefly used to manufacture rotationally symmetric stock materials in standard sizes for further machining, rather than shaped parts tailored to a particular end-use.
Gravity Die Casting – Die casting is a metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mould cavity. The mould cavity is created using two hardened tool steel dies which have been machined into shape and work similarly to an injection mould during the process. Most die castings are made from non-ferrous metals, specifically zinc, copper, aluminium, magnesium, lead, pewter, and tin-based alloys. Depending on the type of metal being cast, a hot- or cold-chamber machine is used. The casting equipment and the metal dies represent large capital costs, and this tends to limit the process to high-volume production. Manufacture of parts using die casting is relatively simple, involving only four main steps, which keeps the incremental cost per item low. It is especially suited for a large quantity of small- to medium-sized castings, which is why die casting produces more castings than any other casting process. Die castings are characterized by a very good surface finish and dimensional consistency.
Investment Casting – Investment casting is an industrial process based on lost-wax casting, one of the oldest known metal-forming techniques. The term “lost-wax casting” can also refer to modern investment casting processes. Investment casting has been used in various forms for the last decades. In its earliest forms, beeswax was used to form patterns necessary for the casting process. Today, more advanced waxes, refractory materials and specialist alloys are typically used for making patterns. Investment casting is valued for its ability to produce components with accuracy, repeatability, versatility and integrity in a variety of metals and high-performance alloys. The fragile wax patterns must withstand forces encountered during the mould making. Much of the wax used in investment casting can be reclaimed and reused. Many materials are suitable for investment casting; examples are stainless steel alloys, brass, aluminium, carbon steel and glass. The material is poured into a cavity in a refractory material that is an exact duplicate of the desired part. Due to the hardness of refractory materials used, investment casting can produce products with exceptional surface qualities, which can reduce the need for secondary machine processes. It can be more expensive than die casting or sand casting, but per-unit costs decrease with large volumes. Investment casting can produce complicated shapes that would be difficult or impossible with other casting methods. It can also produce products with exceptional surface qualities and low tolerances with minimal surface finishing or machining required.
Sand Casting – also known as sand moulded casting, is a metal casting process characterized by using sand as the mould material. The term “sand casting” can also refer to an object produced via the sandcasting process. Over 60% of all metal castings are produced via sand casting process. Moulds made of sand are relatively cheap, and sufficiently refractory even for steel foundry use. In addition to the sand, a suitable bonding agent (usually clay) is mixed or occurs with the sand. The mixture is moistened, typically with water, but sometimes with other substances, to develop the strength and plasticity of the clay and to make the aggregate suitable for moulding. The sand is typically contained in a system of frames or mould boxes known as a flask. The mould cavities and gate system are created by compacting the sand around models called patterns.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION OF CASTINGS
| Sl. No. | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Type | Investment casting, Sand casting, Pressure die casting, Gravity mold castings, Centrifugal casting |
| 2 | MOC | GI/DI/Carbon Steel/Alloy Steel/SS/Copper Alloys/Nickel Alloys/Aluminium/Zinc Alloys |
| 3 | Finished weight range | 2 – 20 MT |
| 4 | Surface quality | ISO R 468, DIN 4769, VSM10321 |
| 5 | Machining | Excess metal is removed, surfaces are finished, castings are heat treated. |
| 6 | Testing | Chemical analysis, Visual inspection, Physical test, corrossion test, mechanical porosity test |
Application

Chemicals industry

Fats and fertiliser industry

Shipbuilding

Construction industry

Oil and Gas industry
Power Plants industry
Steel industry