FORGING
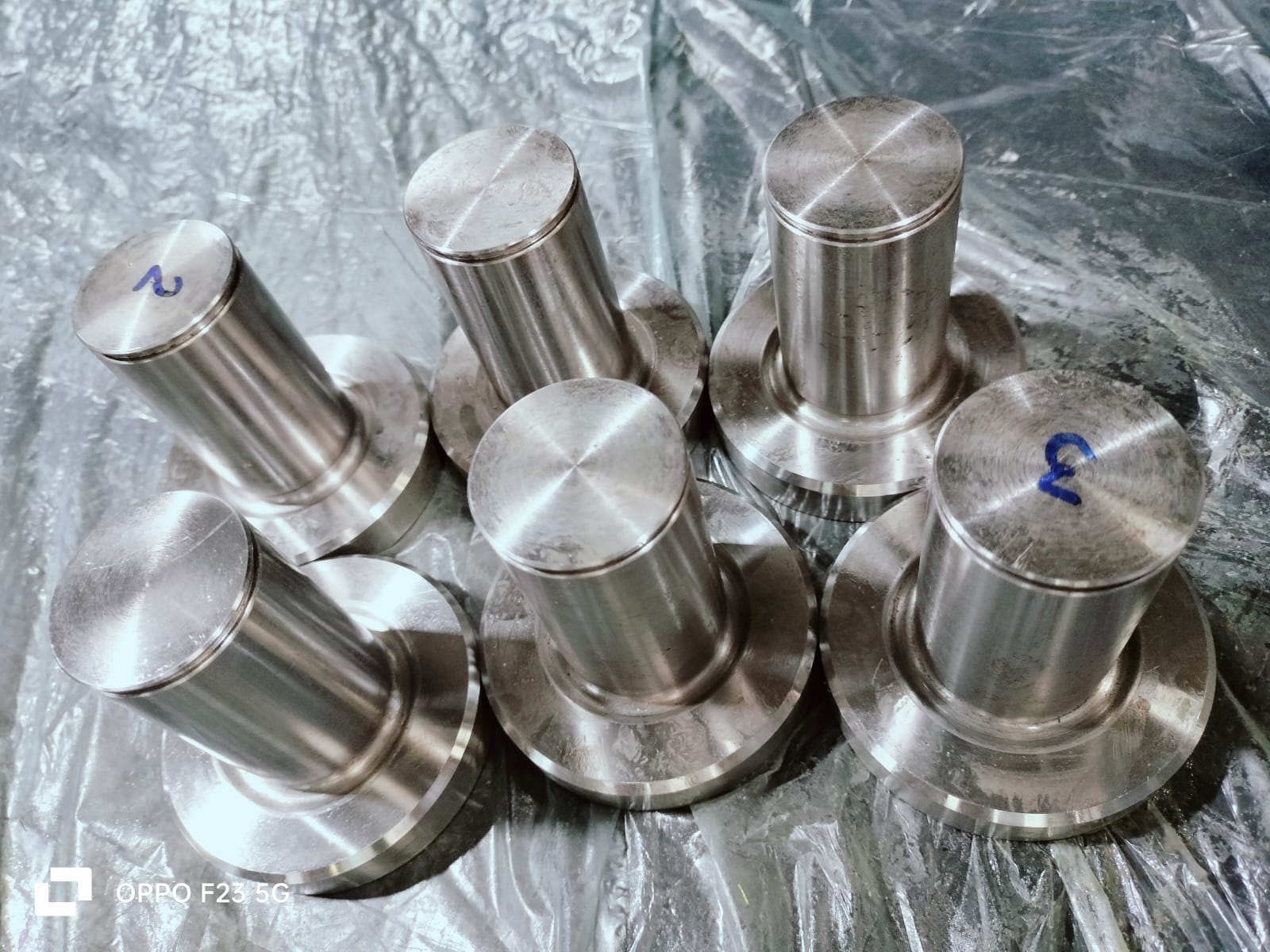

Forging is a manufacturing process that involves shaping metal using localized compressive forces. It's a technique dating back centuries, known for producing strong, reliable, and high-quality metal components. The process typically involves heating the metal above its recrystallization temperature and then applying compressive force through hammering, pressing, or rolling to deform it into the desired shape.
Forging offers several advantages, including improved grain structure, enhanced strength, and better mechanical properties compared to cast or machined parts. There are various forging methods, such as open-die forging, closed-die forging, and impression-die forging, each suited to different shapes, sizes, and production volumes.
Forged components are critical in industries like automotive, aerospace, oil and gas, and construction for applications requiring robust, durable parts, such as gears, shafts, crankshafts, and connecting rods. Advancements in forging technology, including computer simulations, hydraulic presses, and automated systems, continue to refine the process, ensuring higher precision, faster production, and the ability to forge intricate shapes with exceptional strength and reliability.